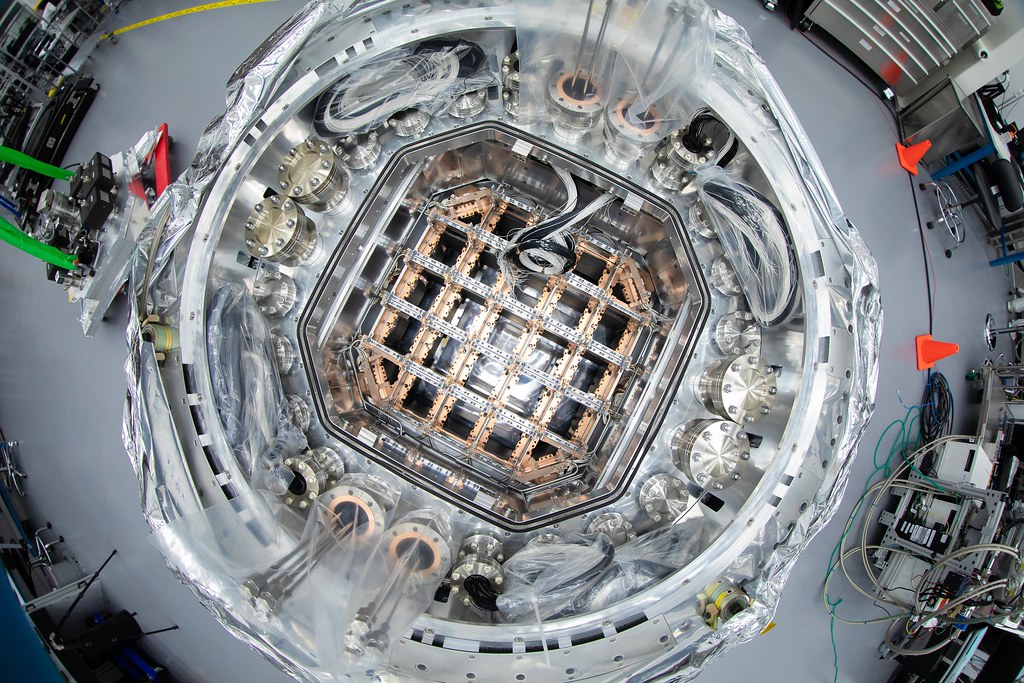
One cool camera: LSST’s cryostat assembly completed
The LSST cryostat, now fully assembled, will keep the camera’s image sensors continuously cooled to minus 150 degrees Fahrenheit for crisp, high-sensitivity views of the night skies.
By Andy Freeberg & Farrin Abbott

LSST’s Cryostat Assembly Completed
This video highlights recent work on the cryostat for the LSST Camera of NSF–DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory.
Farrin Abbott/SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
Work on the camera for the future Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) has reached a major milestone with the completion and delivery of the camera’s fully integrated cryostat. With 3.2 gigapixels, the LSST camera will be the largest digital camera ever built for ground-based astronomy. It’s being assembled at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
The cryostat provides the optical bench — a silicon carbide grid — that keeps the large focal plane, which is 65 centimeters in diameter and composed of 189 CCD imaging sensors, flat to within just a tenth of the width of a human hair, while uniformly cooling it to minus 150 degrees Fahrenheit. It also provides cooling (to minus 30 degrees Fahrenheit) for the sensors' readout electronics, which reside just behind the focal plane. And finally it maintains all this hardware in a clean, contaminant-free, high-vacuum environment.
With the LSST camera, scientists will be able to capture images of the entire Southern sky every few days for a period of 10 years, which will produce petabytes of unprecedented astrophysical data.
The cryostat is now located in LSST’s primary clean room at SLAC, where it’s undergoing vacuum testing. The entire camera is scheduled to be shipped to its final home on a mountaintop in Chile in 2020.

Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, Calif., SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
Financial support for LSST comes from the National Science Foundation (NSF) through Cooperative Agreement No. 1258333, the Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science under Contract No. DE-AC02-76SF00515, and private funding raised by the LSST Corporation. The NSF-funded LSST Project Office for construction was established as an operating center under management of the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA). The DOE-funded effort to build the LSST camera is managed by the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory (SLAC). Learn more at lsst.org.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.